- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Cellular Extract Preparation for Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity Assay
Published: Vol 3, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.811 Views: 25596
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Streamlining Protein Fractional Synthesis Rates Using SP3 Beads and Stable Isotope Mass Spectrometry: A Case Study on the Plant Ribosome
Dione Gentry-Torfer [...] Federico Martinez-Seidel
May 5, 2024 2804 Views
An Activity-Based Proteomics with Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) for Identifying Target Proteases in Arabidopsis Apoplastic Fluid
Sayaka Matsui and Yoshikatsu Matsubayashi
Mar 5, 2025 1878 Views
Advancing 2-DE Techniques: High-Efficiency Protein Extraction From Lupine Roots
Sebastian Burchardt [...] Emilia Wilmowicz
Oct 5, 2025 1681 Views
Abstract
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) acts as a primary defence against reactive oxygen species (ROS) by converting O2- to O2 and H2O2. Members of this enzyme family include CuZnSOD, MnSOD and FeSOD. Most eukaryotes harbor CuZnSOD and MnSOD, and FeSOD is found in plants and prokaryotes. This protocol is to demonstrate how to prepare the cellular extract for the identification and characterization of SODs in planta.
Keywords: SODMaterials and Reagents
- Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N6876 )
- Riboflavin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R4500 )
- N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9281 )
- KCN (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 60178 )
- H2O2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 349887 )
- NBT solution (see Recipes)
- Grinding buffer (see Recipes)
- Riboflavin solution (see Recipes)
- KCN solution (see Recipes)
- H2O2 solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- A light box (white light)
- Centrifuge (Heraecus, Biofuge fresco)
- Protein gel cassette
Procedure
- Arabidopsis cellular extract preparation
- Arabidopsis seedlings were grown at 23 °C with 16 h of light at 60–100 μmol m-2 s-1. Nine-day-old seedlings were collected and weighted.
- Seedlings were homogenized with ice-cold Grinding buffer (tissue weight/buffer volume = 1 mg/3 μl).
Note that the tissue and extract should be kept at 4 °C during all extraction processes. - Centrifuge at 16,000 x g at 4 °C for 10 min.
- The supernatant is the resulting cellular extract, and the amount of protein was quantified by Bradford method (1976).
- Arabidopsis seedlings were grown at 23 °C with 16 h of light at 60–100 μmol m-2 s-1. Nine-day-old seedlings were collected and weighted.
- SOD activity staining
- Proteins or cellular extract (15 to 25 μg) was subjected to 10% native-PAGE at 4 °C.
- Wash the gel with distilled water for 3 times.
- Incubate with NBT solution in dark with shaking for 15 min at room temperature (RT).
- Pour off the NBT solution, wash the gel with distilled water for 3 times.
- Incubate with Riboflavin solution in dark with shaking for 15 min at RT.
- Pour off the Riboflavin solution, wash the gel with distilled water for 3 times.
- Gel was illuminated with a white-light box for 10-15 min at RT. During illumination, immerse gel in a thin layer of distilled water to avoid drying the gel.
- Under light exposure, the riboflavin is reduced then leading the production of O2-. NBT is reduced by O2- to form formazan, a dark blue color precipitate. The enriched SOD activity scavenges the O2- to prevent the formation of formazan, thus, the white SOD activity bands appear in the blue background.
- Proteins or cellular extract (15 to 25 μg) was subjected to 10% native-PAGE at 4 °C.
- Identification of different SOD species (Figure 1)
- KCN treatment: KCN inhibits the CuZnSOD activity only.
All procedures are the same as SOD activity staining processes except the addition of KCN to final 8 mM in Riboflavin solution. - H2O2 treatment: H2O2 inhibits both CuZnSOD and FeSOD activities.
After native-PAGE and prior to NBT staining of SOD activity staining processes, soak the gel with 8 mM H2O2 solution for 30 min with shaking at room temperature. Wash the gel with distilled water for 3 times, and follow the remaining processes of SOD activity staining.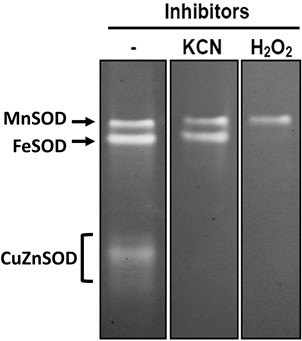
Figure 1. SOD activity verification in Arabidopsis thaliana. KCN is an inhibitor of CuZnSOD activity, whereas H2O2 inhibits both CuZnSOD and FeSOD activities. MnSOD activity is not inhibited by either treatment.
- KCN treatment: KCN inhibits the CuZnSOD activity only.
Recipes
- Grinding buffer
150 mM Tris (pH 7.2) - NBT solution
0.1% NBT dissolved in distilled water.
Store in 4 °C in dark - Riboflavin solution (freshly prepare before use)
28 μM riboflavin and 28 mM TEMED in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0). - 2 N KCN solution
KCN in distilled water. Store in 4 °C. - 8 mM H2O2 solution (freshly prepare before use)
Add 27 μl H2O2 (35%) into 30 ml 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0).
References
- Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248-254.
- Kuo, W. Y., Huang, C. H., Liu, A. C., Cheng, C. P., Li, S. H., Chang, W. C., Weiss, C., Azem, A. and Jinn, T. L. (2013). CHAPERONIN 20 mediates iron superoxide dismutase (FeSOD) activity independent of its co-chaperonin role in Arabidopsis chloroplasts. New Phytol 197(1): 99-110.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kuo, W., Huang, C., Shih, C. and Jinn, T. (2013). Cellular Extract Preparation for Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity Assay. Bio-protocol 3(13): e811. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.811.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











