Articles In Press
"Articles In Press"是经过同行评审并被接受发表的文章。在正式发表之前还可能有内容修改,但可以使用DOI对文章进行引用。正式发表后,该文章将不再在此处展示,现有链接将自动重定向到文章的最终版本。
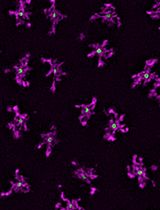
Radial Profile-Based Quantification of Centrosomal Proteins
Centrosomes are dynamic organelles critical for mitotic spindle assembly and cilia formation. Here, I describe a protocol for quantifying relative centrosomal protein abundance in Drosophila melanogaster embryos using radial profile analysis of fluorescence intensity. The method involves embryo collection, manual dechorionation, mounting for live imaging, confocal microscopy, and subsequent image analysis. Radial profiling allows quantification of relative protein abundance together with its spatial distribution at the centrosome, providing either relative or normalized intensity profiles. I then outline how this approach can be integrated with complementary techniques such as fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) and super-resolution imaging, in this case, three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM). Combining radial fluorescence profiling with these imaging modalities enables high-resolution, quantitative analysis of dynamic centrosome assembly in a genetically tractable system.
A Cytosine Deaminase–Based Genomic Footprinting Assay (cFOOT-seq) for Detecting Transcription Factor Occupancy
Transcription factors (TFs) regulate gene expression by binding to cis-regulatory elements in the genome. Understanding transcriptional regulation requires genome-wide characterization of TF occupancy across different chromatin contexts, yet simultaneous assessment of TF binding for multiple factors remains technically challenging. Here, we describe a detailed and reproducible protocol for cFOOT-seq, a cytosine deaminase–based genomic footprinting assay by sequencing, which enables antibody-independent, base-resolution profiling of chromatin accessibility, nucleosome organization, and TF occupancy. In cFOOT-seq, the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) cytosine deaminase SsdAtox converts cytosine to uracil in accessible chromatin, whereas TF binding and nucleosome occupancy locally protect DNA from deamination. Using the FootTrack analysis framework, deamination patterns generated by cFOOT-seq are quantitatively analyzed to derive standardized footprint and chromatin organization profiles at base resolution across the genome. Because cFOOT-seq preserves genomic DNA integrity during deamination-based footprinting, it is compatible with ATAC-seq-based chromatin enrichment. ATAC-combined implementations reduce sequencing depth requirements and improve scalability for footprint-focused analyses, supporting applications in low-input and single-cell settings. This protocol provides a practical framework for genome-wide TF footprint profiling and can be readily applied to dissect gene regulatory mechanisms in development, immunity, and disease, including cancer.
A Bioinformatics Workflow to Identify eccDNA Using ECCFP From Long-Read Nanopore Sequencing Data
Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is a type of circular DNA that exists independently of chromosomes and has garnered significant attention in various fields, particularly in the context of smaller eccDNAs, which have considerable roles in gene regulation through various mechanisms. Current methods such as Circle-Seq and 3SEP can enrich small eccDNAs during sample preparation, but most bioinformatics pipelines remain challenging, exhibiting low accuracy and efficiency. This protocol describes the detailed workflow of a newly developed bioinformatics analysis pipeline, named EccDNA Caller based on Consecutive Full Pass (ECCFP), to accurately identify eccDNA from long-read Nanopore sequencing data. Compared to other pipelines, ECCFP significantly improves detection sensitivity, accuracy, and runtime efficiency. The process includes raw data quality control, trimming of adapters and barcodes, alignment to a reference genome, and identification of eccDNA, with detailed results encompassing accurate positioning of eccDNA, consensus sequences, and variants of individual eccDNA.
A Rapid and Visual Soybean Hairy Root Transformation Protocol Using the RUBY Reporter
Agrobacterium rhizogenes–mediated hairy root transformation provides a rapid platform for gene function analysis prior to stable whole-plant transformation. However, most existing hairy root transformation methods rely on tissue culture and require chemical or fluorescence-based selection, which increases experimental complexity. Here, we describe a tissue culture–free soybean hairy root transformation protocol incorporating the RUBY visual reporter system. While this work does not introduce a new transformation concept, it presents a streamlined implementation of established soybean hairy root methodologies that emphasizes procedural simplicity, reduced handling, and faster access to functional root material. Transgenic roots expressing RUBY can be directly identified by red pigmentation with the naked eye. In RUBY-positive roots, candidate genes driven by the CaMV 35S promoter showed higher expression levels than those in empty-vector controls, indicating that the system supports effective gene expression. Using this procedure, clearly identifiable transgenic hairy roots can be obtained within 20 days. Overall, this protocol simplifies induction and screening while reducing operational complexity and equipment requirements.
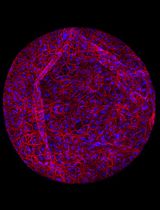
A Guide to Reproducible Cellulose Synthase Density and Speed Measurements in Arabidopsis thaliana
Cellulose synthase complexes (CSCs) play a central role in plant cell wall formation. Their dynamic behavior at the plasma membrane leads to the deposition of cellulose microfibrils into the apoplastic space, thereby shaping the architecture and mechanical properties of the cell wall. Although previous imaging studies have provided important insights into CSC dynamics and localization, standardized and reproducible workflows for quantitative measurements of CSC speed and density remain limited. Here, we present a reproducible live-cell imaging and analysis workflow for quantifying the speed and density of fluorescently labeled CSCs at the plasma membrane in Arabidopsis thaliana. The protocol integrates optimized spinning-disk confocal imaging, surface-based projection of z-stack recordings, automated detection of diffraction-limited CSCs foci, and kymograph-based speed measurements using freely available tools in Fiji. While selected steps, such as region of interest definition and parameter selection for spot detection or trajectory analysis, remain user-guided, these decisions are constrained to well-defined stages within an otherwise standardized pipeline, thereby reducing variability and improving reproducibility across experiments. The workflow has been validated across multiple tissues, reporter lines, genetic backgrounds, and perturbation conditions in Arabidopsis and enables robust comparative analysis of CSC dynamics. Beyond CSCs, this workflow is expected to be adaptable to other fluorescently labeled proteins that appear as diffraction-limited foci at or near the plasma membrane.
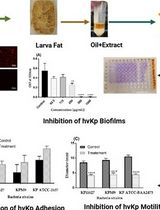
Framework for Analyzing the Anti-biofilm and Anti-virulence Activities of Fatty Acids from Hermetia illucens Larvae Targeting Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
分析黑水虻幼虫脂肪酸对多重耐药肺炎克雷伯菌抗生物膜与抗毒力作用的研究框架
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance and the persistence of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms represent significant challenges to public health. Hermetia illucens (HI) larvae are considered a sustainable reservoir of novel bioactive compounds. This protocol details a method for extracting fatty acids from HI larvae fat (AWME3 fraction) and studying their effects on multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. Effects are evaluated by crystal violet and ethidium bromide uptake assays, motility assays (swimming, swarming, and twitching), minimal biofilm inhibitory and eradication concentration tests (MBIC/MBEC) for single, mixed, and mature biofilms, light, fluorescence, and scanning electron microscopy imaging, and microbial adhesion to solvents (MATS). This protocol offers a reliable methodology for evaluating the anti-biofilm and anti-virulence properties of natural compounds.
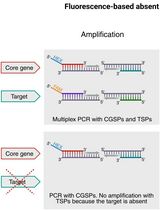
Fluorescence-Based Absent Allele-Specific Amplification (FAASA) for High-Throughput Detection of Absent Alleles
In wheat and other crops, some genes display presence/absence variation, and it is occasionally beneficial to select for the absent allele to remove a functional gene. However, current high-throughput genotyping methods used to detect the absence of genes tend to be inconsistent and inconclusive. Kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) and PCR allele competitive extension (PACE) are two well-established methods for allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR) assays, each using fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to generate a signal for each allele, typically targeting biallelic single-nucleotide polymorphisms. KASP and PACE methods are more difficult to apply to alleles with presence/absence variation because the lack of amplification of the absent allele is indistinguishable from a failed PCR. Here, we present a multiplex fluorescence-based absent allele–specific amplification (FAASA) method using the PACE marker system (compatible with KASP markers) to detect the absence of one particular or all alleles of a target sequence using a primer mix consisting of one target-specific primer pair (TSP) and a second primer set specific to a highly conserved endogenous gene known as a core gene–specific primer pair (CGSP). The forward primer of each pair is tagged with a 5′ terminal tail complementary to dye-labeled oligonucleotides in commercially available FRET cassettes. Lines that amplify only the core gene do not carry the target, while lines that amplify both the core gene and the target carry alleles of both the core gene and the target. The inclusion of the CGSPs allows researchers to confidently distinguish lines with absent alleles of the target from lines with failed PCR reactions, which can happen due to various reasons, including inadequate DNA quality or quantity.
Development, Expansion, and Histological Characterization of Patient-Derived Liver Organoids for Drug Screening and Disease Modeling
用于药物筛选与疾病建模的患者来源肝脏类器官的建立、扩增及组织学特征分析
Organoids are self-organizing 3D tissues representing an innovative technology with interesting implications and potential for the study of tumor biology. They can be developed from fine-needle biopsies or resection material from healthy or tumor tissues. Patient-derived organoids are able to retain most of the histological characteristics, the expression profile, and the genomic landscape of the corresponding primary tissues, making them suitable for translational studies and for the identification of molecular alterations in the field of personalized medicine. Here, we describe a detailed protocol for the preparation and in vitro expansion of tumor and non-tumor organoids from surgical resections or needle biopsies of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), enabling subsequent testing of small-molecule VDAC1 antagonists at different doses. In parallel, we developed a hepatic steatosis model by treating healthy liver organoids with oleic acid, recapitulating key features of lipid accumulation and metabolic dysfunction in vitro. This protocol enables the generation of patient-derived liver organoids that preserve the histological and molecular characteristics of their original tissue, providing a robust and versatile platform for translational studies, personalized drug testing, and the exploration of novel therapeutic strategies targeting tumor metabolism.
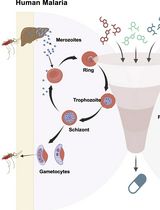
A Standardized Culture Medium for Comparative Drug Efficacy Evaluation Across Plasmodium and Babesia Species
用于疟原虫与巴贝虫药效比较评价的标准化培养基体系
The discovery of broad-spectrum antiparasitic agents relies on the ability to evaluate drug efficacy under harmonized in vitro conditions across related species. However, current drug screening pipelines for intraerythrocytic parasites are constrained by the use of species-specific media with distinct nutrient compositions and serum sources, which hinder direct comparison of compound potency. To address this gap, we describe a unified erythrocytic culture system based on DMEM/F12 supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (DFS20), which supports robust asexual growth of multiple Plasmodium falciparum strains (3D7, Dd2, HB3, V1/S), Babesia duncani, Babesia divergens (Rouen 87), and Babesia MO1. Parasite proliferation and morphology in DFS20 are comparable to those observed in established species-specific media such as RPMI-1640 for P. falciparum and B. divergens and HL-1/Claycomb/DMEM/F12/SFM for B. duncani, while eliminating reliance on undefined or discontinued proprietary components. Importantly, this standardized medium enables cross-species growth inhibition assays for direct comparison of drug efficacy under identical conditions. Using this platform, we recently screened dihydrotriazines and biguanides targeting the conserved DHFR-TS enzymes and identified potent antifolate candidates with broad-spectrum activity against Babesia and Plasmodium species. For B. duncani, which is uniquely supported by both a continuous in vitro human erythrocyte culture system and a lethal in vivo mouse infection model, integration with the in-culture and in-mouse (ICIM) pipeline enables systematic validation of pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, resistance, and toxicity. This unified DFS20-based system establishes a scalable and reproducible protocol for harmonized drug efficacy evaluation across intraerythrocytic parasites and provides a foundation for the development and prioritization of pan-antiparasitic therapies.
A Rapid and High-Recovery Extracellular Vesicle (EVs) Isolation Technique from Blood Samples
一种快速高回收率的血液样本细胞外囊泡分离方法
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) circulating in blood serve as non-invasive “liquid biopsies,” carrying molecular cargo that reflects the physiological and pathological state of distant cells. Their analysis is crucial for understanding disease mechanisms and discovering novel biomarkers. Clinically, blood EVs hold significant promise for early disease diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and monitoring treatment response in diverse areas such as organ transplantation, cancer, and neurological disorders. Current EV isolation techniques, beyond ultracentrifugation, include size exclusion chromatography (separation by size for high purity) and immunoaffinity capture (using antibodies for high specificity). Here, we present a simplified, rapid, and reproducible method for isolating EVs from small-volume blood samples. This protocol consistently yields a concentrated EV pellet covering 50–300 nm EVs, amenable to direct downstream analysis. Developed and validated in our laboratory using human, porcine, and murine blood samples, this method has proven instrumental in identifying EV-based biomarkers for predicting outcomes related to organ transplantation. The protocol’s adaptability and reliance on readily prepared, cost-effective reagents further enhance its utility. This scalable approach can be further integrated with subsequent purification or enrichment steps to optimize sample preparation for protein and nucleic acid assays.
Obtaining Chondroprogenitors (Articular Cartilage-Derived Cells) via Explant Methodology
采用组织块培养法获取软骨祖细胞(来源于关节软骨)
Obtaining articular cartilage-derived cells (chondroprogenitors) by explant methodology is a reliable approach for isolating migratory progenitor cells that retain strong chondrogenic potential. This method allows cells to emerge naturally from small cartilage fragments without enzymatic digestion. The procedure consists of plating cartilage explants on a plastic surface with culture medium, from which cells subsequently migrate and adhere to the substrate. Compared with enzymatic isolation, the explant approach minimizes cellular stress and better reproduces the physiological microenvironment of cartilage tissue. This protocol can be applied to both osteoarthritic and non-osteoarthritic samples, enabling comparative studies on disease-related phenotypic differences. Overall, this technique offers a reproducible, straightforward, and minimally invasive strategy for obtaining functional chondroprogenitor cells suitable for cartilage regeneration research.
Simple Induction and Detection of Anthocyanins in Arabidopsis thaliana: A Tool for Mutant Screening and Metabolic Analysis
拟南芥花青素的简易诱导与检测方法:用于突变体筛选与代谢分析
Anthocyanins are specialized flavonoid pigments that play critical roles in plant coloration, photoprotection, and responses to environmental stress. Arabidopsis thaliana serves as a valuable genetic model for dissecting anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulatory networks. Conventional methods for anthocyanin quantification, such as crude spectrophotometric assays, often compromise pigment integrity, yield inconsistent results, and provide limited information on compound composition. Here, we describe a simple, reproducible, and high-fidelity protocol for the induction, extraction, quantification, and chromatographic profiling of anthocyanins in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. The workflow employs well-defined anthocyanin-inductive conditions (AIC), methanol/formic acid extraction, lyophilization for dry-weight normalization, and dual quantification via spectrophotometry and High-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection (HPLC-DAD) analysis. This protocol enables accurate comparison between wild-type and mutant genotypes, facilitating both mutant screening and metabolic pathway analysis. The approach minimizes pigment degradation, enhances reproducibility across replicates, and offers a robust tool for research in plant metabolism, stress physiology, and flavonoid biochemistry.
Machine Learning-Assisted Quantification of Organelle Abundance
基于机器学习的细胞器丰度定量分析方法
Organelle abundance is a key microscopic readout of organelle formation and, in many cases, function. Quantification of organelle abundance using confocal microscopy requires estimating their area based on the fluorescence intensity of compartment-specific markers. This analysis usually depends on a user-defined intensity threshold to distinguish organelle regions from the surrounding cytoplasm, which introduces potential bias and variability. To address this issue, we present a machine learning–assisted algorithm that allows for the quantification of organelle density using the open-source Fiji platform and WEKA segmentation. Our method enables the automated quantification of organelle number, area, and density by learning from training data. This standardizes threshold selection and minimizes user intervention. We demonstrate the utility of this approach for both membrane and non-membrane organelles, such as peroxisomes, lipid droplets, and stress granules, in human cells and whole fish samples.
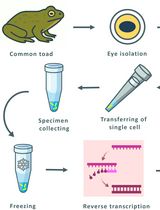
Combining Suction-Pipette Spectral Identification With Single-Cell RT-PCR to Make Differential Analyses of Amphibian Red and Green Rods
结合吸管电极光电流记录与单细胞RT-PCR技术实现两栖动物红视杆与绿视杆的差异分析
Amphibian retinas contain “green” rods, which are rod-shaped photoreceptors with a cone-type visual pigment. These rods are considered a potentially transitional photoreceptor type, but their phototransduction cascade’s molecular composition has remained uncertain. Here, we present a streamlined electrophysiology-molecular workflow that enables the rapid spectral identification, physical capture, and targeted single-cell reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) of individual amphibian photoreceptors. After suction-pipette spectral screening under alternating red and green illumination, electrophysiologically identified cells are isolated and processed directly for reverse transcription and PCR. Coupling real-time functional phenotyping with sensitive molecular profiling provides a practical tool for resolving photoreceptor molecular heterogeneity and investigating evolutionary transitions between rod and cone phenotypes.
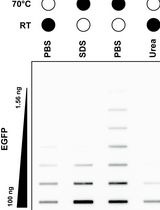
Selective Isolation of TOP3B•mRNA Covalent Intermediates Using Denaturing Oligo-dT Pulldown
利用变性Oligo-dT Pull-down技术选择性分离TOP3B-mRNA共价中间体
The deletion and mutation of Topoisomerase 3β (TOP3B) is linked to multiple neurological disorders and is the only known topoisomerase that is also catalytically active on RNA in vitro and in cells. Uniquely, TOP3B is primarily localized to the cytoplasm, binds to open reading frames of mRNA, and regulates mRNA stability and translation in a transcript-specific manner. A common approach for studying TOP3B activity in cells is immunodetection of TOP3B•RNA covalent intermediates after bulk RNA isolation. However, in this approach, the RNA species is unknown and is not selective for the major TOP3B substrate, mRNA. In this protocol, we describe a recently developed and optimized protocol for capturing TOP3B•mRNA covalent intermediates using oligo-dT isolation of mRNA under protein-denaturing conditions. Covalent intermediates are then detected by a dual membrane slot blotting strategy with nitrocellulose and positively charged nylon membranes. Nitrocellulose membrane-bound TOP3B•mRNA covalent intermediates are analyzed by immunodetection, and nylon membrane-bound free mRNA is stained with methylene blue. The protocol detailed below has been validated with wildtype and mutant 3xFLAG-tagged TOP3B expressed in Neuro2A cells, with additional optimization for slot blotting using recombinant EGFP.
aGPCR-HEK: A Stable High-Expression Inducible Mammalian Cell Expression System for Adhesion GPCR Structural Biology Applications
aGPCR-HEK:用于黏附型 G 蛋白偶联受体结构生物学研究的稳定高表达可诱导哺乳动物细胞表达系统
ADGRL4 is an adhesion G protein–coupled receptor (aGPCR) implicated in multiple tumours. In our experience, conventional insect cell-based baculovirus expression systems have not yielded sufficient correctly folded ADGRL4 protein for purification and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis. Here, we describe aGPCR-HEK, a six-week protocol that establishes stable tetracycline-inducible mammalian HEK293S GnTI- TetR cell lines expressing N-terminally HA- and GFP-tagged aGPCRs. The method comprises lentiviral production in Lenti-X 293T cells, transduction of target adherent HEK293S GnTI- TetR cells, flow cytometry enrichment of uninduced GFP-positive cells displaying leaky expression, adaptation to suspension culture, and large-scale tetracycline induction and harvesting of cells for downstream purification and cryo-EM. The system yields reproducible, milligram-scale quantities of folded aGPCR suitable for structural and biochemical studies.
Spatial Proteomics Using S4P
基于 S4P 的空间蛋白质组学研究方法
Spatial proteomics enables the mapping of protein distribution within tissues, which is crucial for understanding cellular functions in their native context. While spatial transcriptomics has seen rapid advancement, spatial proteomics faces challenges due to protein non-amplifiability and mass spectrometry sensitivity limitations. This protocol describes a sparse sampling strategy for spatial proteomics (S4P) that combines multi-angle tissue strip microdissection with deep learning–based image reconstruction. The method achieves whole-tissue slice coverage with significantly reduced sampling requirements, enabling mapping of over 9,000 proteins in mouse brain tissue at 525 μm resolution within 200 h of mass spectrometry time. Key advantages include reduced sample processing time, deep proteome coverage, and applicability to centimeter-sized tissue samples.
High-Resolution Quantification of Two-Way Nanobody Synergy Using Automated Liquid Handling and Computational Modeling
结合自动化液体处理与计算建模的双向纳米抗体协同作用高分辨率定量分析
Evaluating single-domain antibody cooperativity is essential for developing potent, escape-resistant antiviral biologics. Here, we present a protocol that reproducibly quantifies functional synergy between neutralizing nanobody pairs in standardized viral infectivity assays. Controlled automated liquid handling prepares two-dimensional concentration matrices, minimizing pipetting variance and systematic error. Neutralization data are fitted using quantitative models that independently estimate potency, cooperativity, and efficacy to distinguish additive, synergistic, and antagonistic effects between nanobody pairs. Replicated measurements enable statistically interpretable parameter estimates, supporting robust evaluation of combinatorial nanobody therapeutics with commonly available equipment and open-source analysis tools. This framework is broadly applicable to assessing cooperative effects among other classes of binding or inhibitory molecules, facilitating systematic discovery of synergistic combinations.
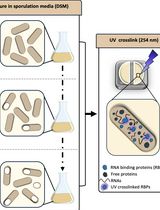
Dynamic Mapping of RNA-Binding Proteins During Bacillus subtilis Sporulation Using Orthogonal Organic Phase Separation
基于正交有机相分离技术动态解析枯草芽孢杆菌孢子形成过程中 RNA 结合蛋白图谱
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) have pleiotropic roles in modulating the physiology of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, enabling them to adapt to environmental variations. The importance of RBPs has led to the development of a variety of methods aiming to identify them. However, most of these approaches have primarily been implemented and optimized in eukaryotic systems. To both uncover novel RBPs involved in Bacillus subtilis sporulation and capture their RNA-binding ability dynamically, we adapted the orthogonal organic phase separation technique (OOPS), which had previously been used in Escherichia coli to reveal its RNA-binding proteome (RBPome). We optimized the UV cross-linking process used to stabilize RNA–protein interactions in vivo and the bacterial lysis process to overcome the robust cell wall of Gram-positive sporulating cells. RNA–protein complexes are then recovered after phase separation steps using guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform, and RNA-associated proteins are identified and label-free-quantified by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Collecting samples at various time points during sporulation further enables tracking the dynamics of the RBPome. In addition to being applicable to bacteria and requiring minimal starting material, this method has provided a comprehensive map of the RBPome during sporulation, refining the roles of known factors and revealing new players.
Quantifying Lysosomal Degradation of Extracellular Proteins With a Fluorescent Protein-Based Internalization Assay
基于荧光蛋白内吞检测体系定量分析溶酶体对细胞外蛋白的降解
Endocytosis is an essential membrane transport mechanism that is indispensable for the maintenance of life. It is responsible for the selective internalization and subsequent degradation or recycling of specific extracellular proteins and nutrients, thereby facilitating cellular nutrient supply, modulation of receptor signaling, and clearance of foreign substances. However, methods for the quantitative analysis of lysosomal degradation of extracellular proteins via endocytosis remain limited. This protocol describes a method for purifying the protein-of-interest (POI)–red fluorescent protein (RFP)–green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion protein, which is modified with specific mammalian cell glycans or other modifications, from the conditioned medium of mammalian cell cultures. Subsequently, the protocol details a quantitative approach for evaluating its internalization and lysosomal degradation within cells using the RFP–GFP tandem fluorescent reporter. Following the addition of POI-RFP-GFP to the medium, cells can be subjected to cell biological assays, such as flow cytometry, as well as biochemical analyses, such as immunoblotting. This protocol is broadly applicable to studies of the internalization of extracellular proteins.
Reconstruction of Axonal Projections of Single Neurons Using PointTree
基于 PointTree 的单神经元轴突投射重建方法
The morphology of single-neuron axonal projections is critical for deciphering neural circuitry and information flow in the brain. Yet, manually reconstructing these complex, long-range projections from high-throughput whole-brain imaging data remains an exceptionally labor-intensive and time-consuming task. Here, we developed a points assignment-based method for axonal reconstruction, named PointTree. PointTree enables the precise identification of the individual axons from densely packed axonal population using a minimal information flow tree model to suppress the snowball effect of reconstruction errors. In this protocol, we have elaborated on how to configure the required environment for PointTree software, prepare suitable data for it, and run the software. This protocol can assist neuroscience researchers in more easily and rapidly obtaining the reconstruction results of neuronal axons.
Non-Enzymatic Isolation of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts From Human Prostate Tumor Explants
从人前列腺肿瘤组织块中非酶法分离癌相关成纤维细胞
Prostate carcinoma (PCa) progression is strongly influenced by the surrounding tumor microenvironment, where cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) represent the most abundant and functionally relevant stromal population. Despite their importance, the lack of stable cell lines representing CAF phenotypes limits the study of stromal–tumor interactions. To address this limitation, we provide an optimized protocol for isolating CAFs from fresh human PCa biopsies based on a mechanical procedure exploiting the specific CAF ability to migrate out from the tumor explants. This approach preserves tissue architecture and maintains CAF viability and phenotype. The resulting ex vivo CAF cultures provide a suitable model to investigate CAF biology within the tumor microenvironment.
Simultaneous Immunofluorescence-Based In Situ mRNA Expression and Protein Detection in Bone Marrow Biopsy Samples
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) can be employed to study the expression and subcellular localization of nucleic acids by using labeled antisense strands that hybridize with the target RNA or DNA molecules. Likewise, immunofluorescence antibody staining (IF) takes advantage of the specific interaction between a fluorophore-labeled antibody and its corresponding antigen. This protocol reports the combination of RNA-FISH and IF antibody staining for simultaneous detection of both RNA transcripts and proteins of interest in routine formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) bone marrow biopsy samples. Herein, we provide a detailed description of the methodology that we have developed and optimized to study the spatial expression of two transcripts—TGFB1 and PDGFA1—in human hematopoietic (CD45+) and non-hematopoietic (CD271+) cells in the bone marrow of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
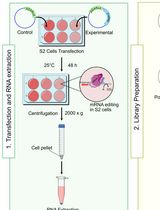
Employing Tribe to Study RNA Interactions of Ataxin-2 in Drosophila S2 Cells
利用 TRIBE 技术研究果蝇 S2 细胞中 Ataxin-2 的 RNA 相互作用
RNA-binding protein (RBP)–RNA interactions are fundamental for gene regulation and cellular homeostasis. Ataxin-2 is an RBP that has been shown to play an instrumental role in pathophysiological processes by binding to mRNA. Methods such as RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), cross-linking immunoprecipitation (CLIP), and their variants can be used to study the interactions between Ataxin-2 and its targets, although their high sample requirements and labor-intensive workflows can limit their widespread use. RNA editing-based approaches, such as targets of RBPs identified by editing (TRIBE), provide effective alternatives. TRIBE enables transcriptome-wide identification of RBP targets by inducing site-specific adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing, which is subsequently detected through high-throughput RNA sequencing in both in vivo and in vitro systems. Compared to in vivo models, cell lines offer a rapid and flexible experimental design. Drosophila S2 cells are a commonly used insect cell line to investigate RNA–protein dynamics and serve as a versatile platform for studying RBP function. Here, we describe a protocol used for identifying RNA targets of Ataxin-2, a versatile RBP involved in post-transcriptional and translational regulation, in S2 cells using TRIBE. This method allows rapid, efficient, and reliable identification of Ataxin-2-associated RNA targets and can be readily applied to other RBPs.
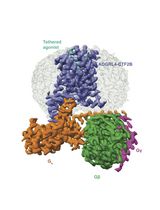
Purification of the Active-State G Protein-Coupled Receptor ADGRL4 for Cryo-Electron Microscopy Using a Modular Tag System and a Tethered mini-Gq
采用模块化标签系统与连接型 mini-Gq 纯化活化状态 G 蛋白偶联受体 ADGRL4 以用于冷冻电镜研究
ADGRL4 is an adhesion G protein-coupled receptor (aGPCR) implicated in tumour progression in multiple malignancies. We recently determined the first cryo-EM structure of active-state ADGRL4, revealing its weak coupling to the heterotrimeric G protein Gq and providing insights into its activation mechanism. Here, we describe a complete modular workflow for purifying active-state ADGRL4 over 2–3 days using a multifunctional tagging strategy incorporating multiple orthogonal detection, purification, and cleavage tags at the N-terminus as well as a tethered mini-Gq at the C-terminus. This configuration enhanced receptor cell-surface expression and stability and allowed different purification strategies to be tested during the development of the purification protocol. Although developed and optimised for ADGRL4, this approach is readily transferable to other weakly coupling aGPCRs or GPCRs where complex stability is a limiting factor for structural analysis.
Using combined fluorescent in situ hybridization with Immunohistochemistry to co-localize mRNA in diverse neuronal cell types
Understanding gene expression within defined neuronal populations is essential for dissecting the cellular and molecular diversity of the brain. mRNA assays provide a direct readout of gene expression, capturing transcriptional changes that may precede or occur independently of protein abundance, whereas protein assays reflect the cumulative effects of translation, modification, and degradation. Moreover, in histological analysis, immunohistochemical protein detection results in visually diffuse labeling, which makes it difficult to quantitatively assess levels and locations of expression at high resolution. Here, we present a protocol that allows for mRNA detection in single neuronal cell types with a high degree of sensitivity and anatomical resolution. This protocol combines fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) with immunohistochemistry (IHC) on the same tissue section. Briefly, FISH is carried out by ACDBio RNAscope® fluorescent in situ hybridization technology, which involves processing the tissue sections, followed by signal amplification. This involves target retrieval, probe hybridization, and signal enhancement. Then, the tissue section is processed for IHC, which involves blocking nonspecific sites and incubation with primary antibodies, followed by development of a fluorescent signal with secondary antibodies. Typically, visual mRNA detection with FISH can be seen as individual puncta, whereas targeting the protein with an antibody results in filled cells or processes. The variation in staining pattern allows for the quantification of distinct mRNA transcripts within different neuronal populations, which renders co-localization analyses easy and efficient.
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for Assessing RNA–Protein Binding and Complex Formation Using Recombinant RNA-Binding Proteins and In Vitro–Transcribed RNA
Evaluating RNA–protein interactions is key to understanding post-transcriptional gene regulation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) remain a widely used technique to study these interactions, revealing information about binding affinities and binding modalities, including cooperativity and complex formation. Here, we detail, in a step-by-step protocol, how to perform EMSAs. We describe how to generate, purify, and quantitate 32P-radiolabeled RNA by in vitro transcription, as well as the expression and purification of recombinant RNA-binding proteins in E. coli using ELAV as an example. We then describe how to set up binding reactions using serial dilutions in a microtiter plate format of recombinant ELAV and in vitro–transcribed RNA and how to perform EMSAs using native low-crosslinked acrylamide gels, with detailed graphically supported instructions and troubleshooting guides.
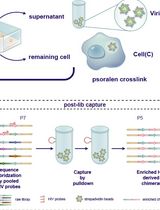
High-resolution mapping of RNA-RNA interactions across the HIV-1 genome with HicapR
基于 HiCapR 的 HIV-1 全基因组 RNA–RNA 相互作用高分辨率图谱构建
The genomes of RNA viruses can fold into dynamic structures that regulate their own infection and immune evasion processes. Proximity ligation methods (e.g., SPLASH) enable genome-wide interaction mapping but lack specificity when dealing with low-abundance targets in complex samples. Here, we describe HiCapR, a protocol integrating in vivo psoralen crosslinking, RNA fragmentation, proximity ligation, and hybridization capture to specifically enrich viral RNA–RNA interactions. Captured libraries are sequenced, and chimeric reads are analyzed via a customized computational pipeline to generate constrained secondary structures. HiCapR generates high-resolution RNA interaction maps for viral genomes. We applied it to resolve the in vivo structure of the complete HIV-1 RNA genome, identifying functional domains, homodimers, and long-range interactions. The protocol's robustness has been previously validated on the SARS-CoV-2 genome. HiCapR combines proximity ligation with targeted enrichment, providing an efficient and specific tool for studying RNA architecture in viruses, with broad applications in virology and antiviral development.
Enhanced RNA-Seq Expression Profiling and Functional Enrichment in Non-model Organisms Using Custom Annotations
Functional enrichment analysis is essential for understanding the biological significance of differentially expressed genes. Commonly used tools such as g:Profiler, DAVID, and GOrilla are effective when applied to well-annotated model organisms. However, for non-model organisms, particularly for bacteria and other microorganisms, curated functional annotations are often scarce. In such cases, researchers often rely on homology-based approaches, using tools like BLAST to transfer annotations from closely related species. Although this strategy can yield some insights, it often introduces annotation errors and overlooks unique species-specific functions. To address this limitation, we present a user-friendly and adaptable method for creating custom annotation R packages using genomic data retrieved from NCBI. These packages can be directly imported as libraries into the R environment and are compatible with the clusterProfiler package, enabling effective gene ontology and pathway enrichment analysis. We demonstrate this approach by constructing an R annotation package for Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, as an example. The annotation package is then utilized to analyze differentially expressed genes from a subset of RNA-seq dataset (GSE292409), which investigates the transcriptional response of M. tuberculosis H37Rv to rifampicin treatment. The chosen dataset includes six samples, with three serving as untreated controls and three exposed to rifampicin for 1 h. Further, enrichment analysis was performed on genes to demonstrate changes in response to the treatment. This workflow provides a reliable and scalable solution for functional enrichment analysis in organisms with limited annotation resources. It also enhances the accuracy and biological relevance of gene expression interpretation in microbial genomics research.
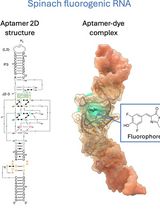
Visualizing diverse RNA functions in living cells with Spinach™ family of fluorogenic aptamers
利用SpinachTM系列荧光适配体可视化活细胞中多种RNA功能
RNA is now recognized as a highly diverse and dynamic class of molecules whose localization, processing, and turnover are central to cell function and disease. Live-cell RNA imaging is therefore essential for linking RNA behavior to mechanism. Existing approaches include quenched hybridization probes that directly target endogenous transcripts but face delivery and sequestration issues, protein-recruitment tags such as MS2/PP7 that add large payloads and can perturb localization or decay, and CRISPR–dCas13 imaging that requires substantial protein cargo and careful control of background and off-target effects. Here, we present a protocol for live-cell RNA imaging using the SpinachTM family of fluorogenic RNA aptamers. The method details the design and cloning of SpinachTM-tagged RNA constructs, selection and handling of cognate small-molecule fluorophores, expression in mammalian cell lines, dye loading, and image acquisition on standard fluorescence microscopes, followed by quantitative analysis of localization and dynamics. We include controls to verify aptamer expression and signal specificity, guidance for multiplexing with related variants (e.g., Broccoli, Corn, Squash, Beetroot), and troubleshooting for dye permeability and signal optimization. Application examples illustrate use in tracking cellular delivery of mRNA therapeutics, monitoring transcription and decay in response to perturbations, and the forming of toxic RNA aggregates. Compared with prior methods, SpinachTM tags are compact, genetically encodable, and fluorogenic, providing high-contrast imaging in both the nucleus and cytoplasm with single-vector simplicity and multiplexing capability. The protocol standardizes key steps to improve robustness and reproducibility across cell types and laboratories.
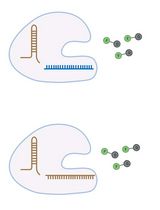
Enhancement of RNA Imaging Platforms by the Use of Peptide Nucleic Acid-Based Linkers
RNA imaging techniques enable researchers to monitor RNA localization, dynamics, and regulation in live or fixed cells. While the MS2-MCP system—comprising the MS2 RNA hairpin and its binding partner, the MS2 coat protein (MCP)—remains the most widely used approach, it relies on a tag containing multiple fluorescent proteins and has several limitations, including the potential to perturb RNA function due to the tag’s large mass. Alternative methods using small-molecule binding aptamers have been developed to address these challenges. This protocol describes the synthesis and characterization of RNA-targeting probes incorporating a peptide nucleic acid (PNA)-based linker within the cobalamin (Cbl)-based probe of the Riboglow platform. Characterization in vitro involves a fluorescence turn-on assay to determine binding affinity (KD) and selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE) footprinting analysis to assess RNA-probe interactions at a single nucleotide resolution. To show the advancement of PNA probes in live cells, we present a detailed approach to perform both stress granule (SG) and U-body assays. By combining sequence-specific hybridization with structure-based recognition, our approach enhances probe affinity and specificity while minimizing disruption to native RNA behavior, offering a robust alternative to protein-based RNA imaging systems.
Amplification-Free Detection of Highly Structured RNA Molecules Using SCas12aV2
The CRISPR/Cas12a system has revolutionized molecular diagnostics; however, conventional Cas12a-based methods for RNA detection typically require transcription and pre-amplification steps. Our group has recently developed a diagnostic technique known as the SCas12a assay, which combines Cas12a with a split crRNA, achieving amplification-free detection of miRNA. However, this method still encounters challenges in accurately quantifying long RNA molecules with complex secondary structures. Here, we report an enhanced version termed SCas12aV2 (split-crRNA Cas12a version 2 system), which enables direct detection of RNA molecules without sequence limitation while demonstrating high specificity in single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) applications. We describe the general procedure for preparing the SCas12a system and its application in detecting RNA targets from clinical samples.